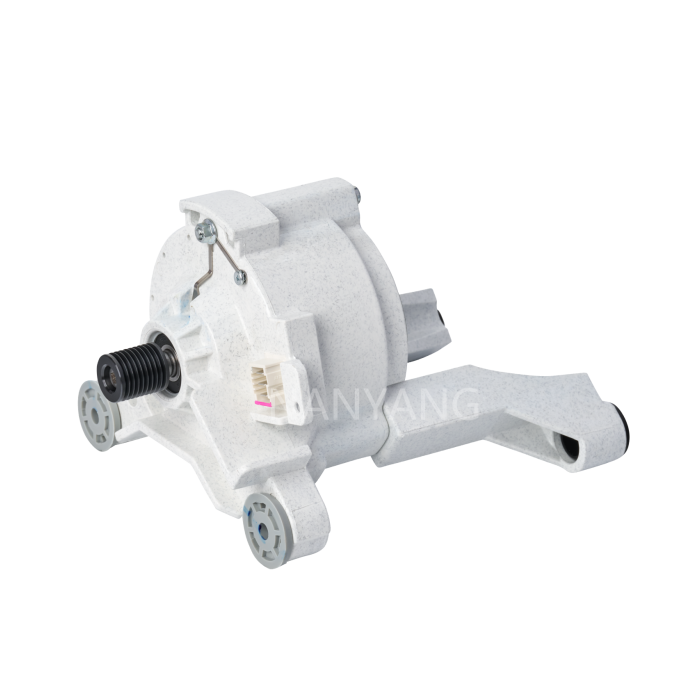
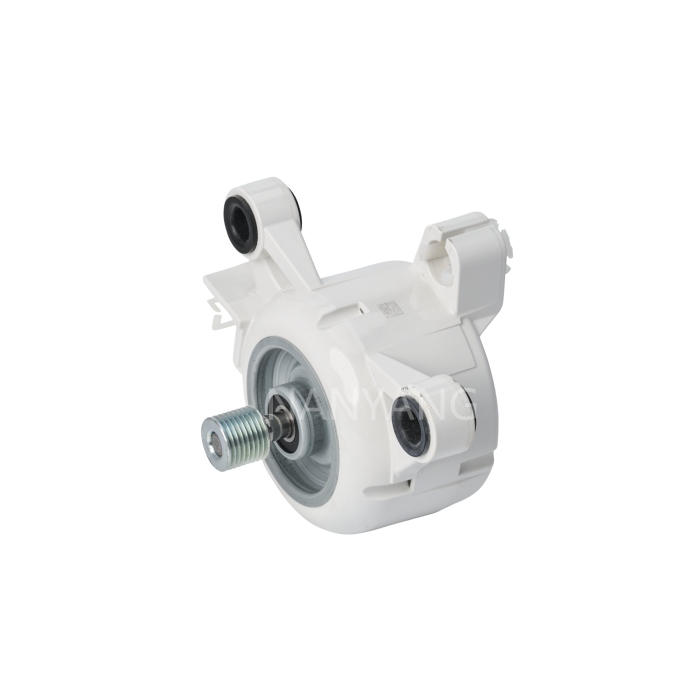
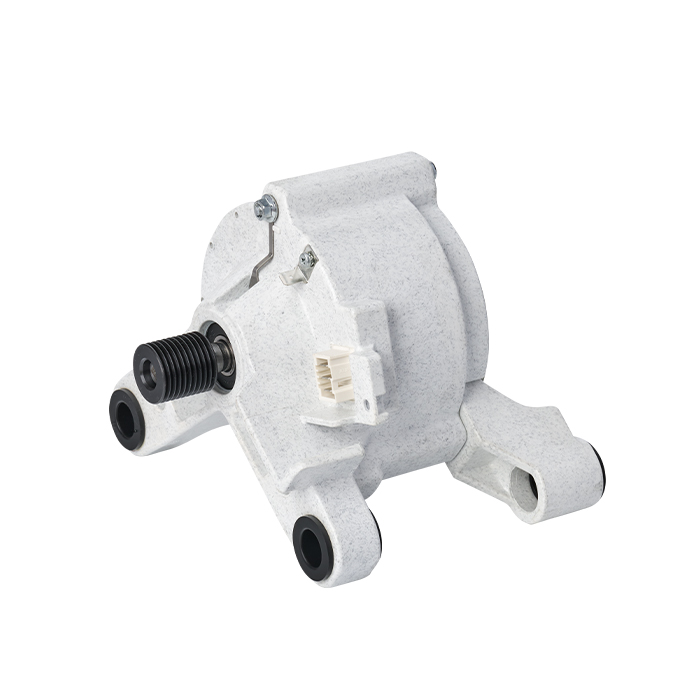
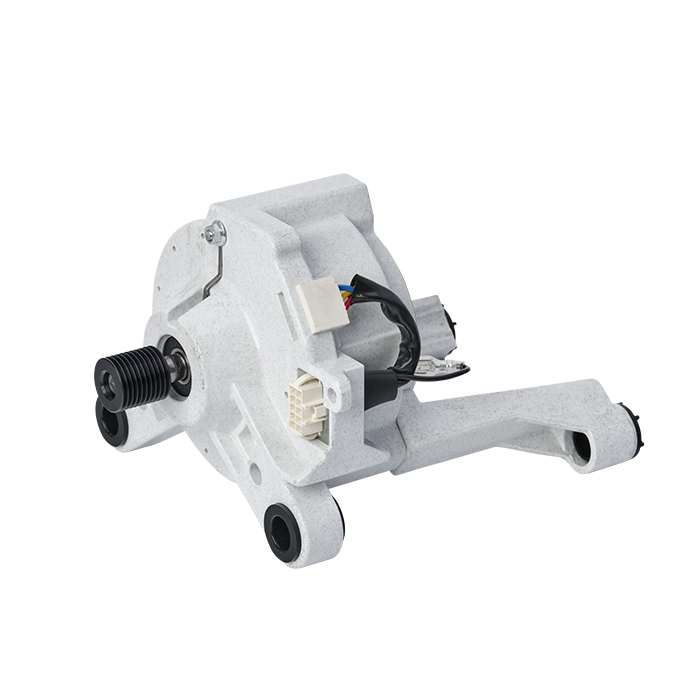
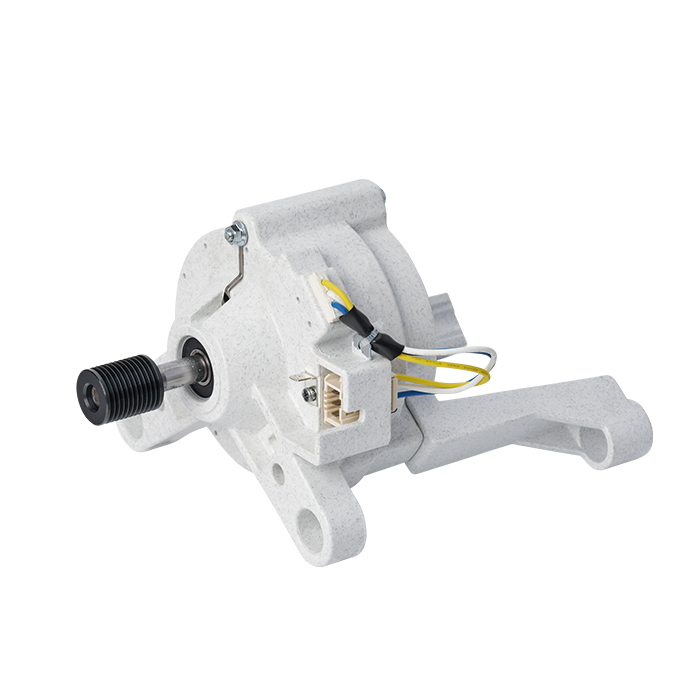
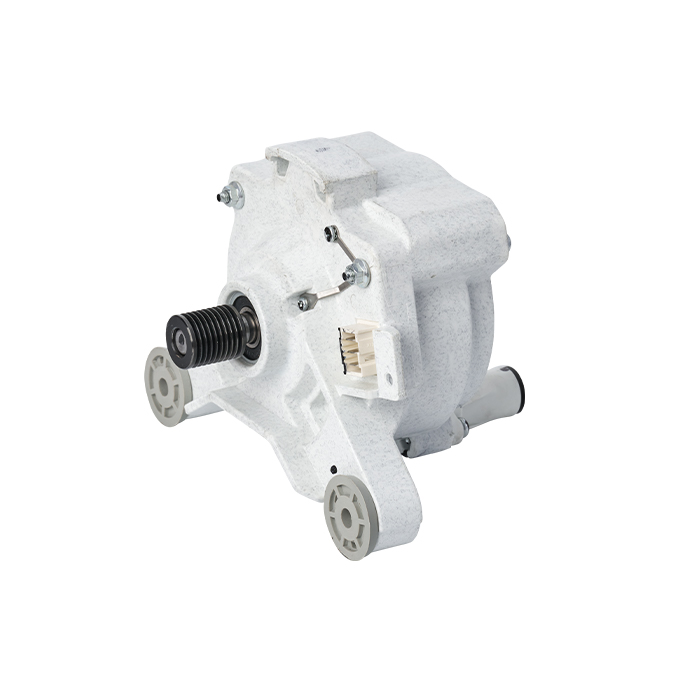
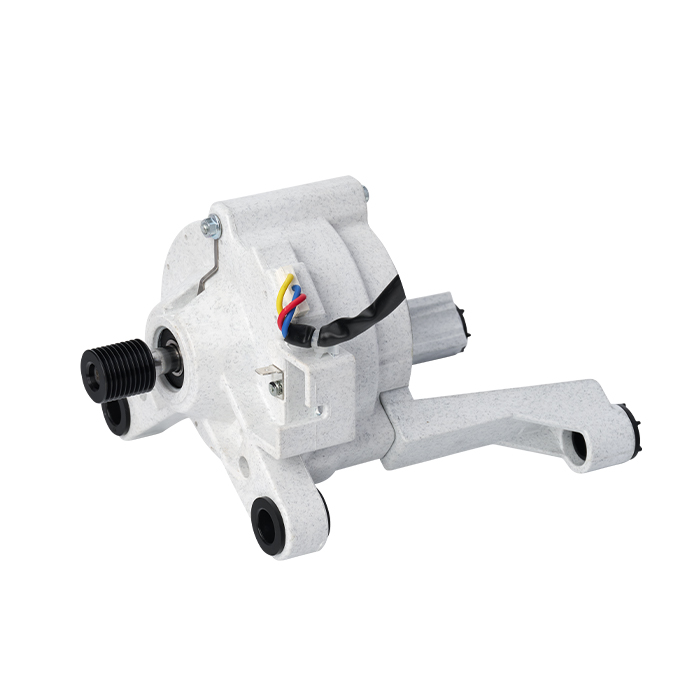
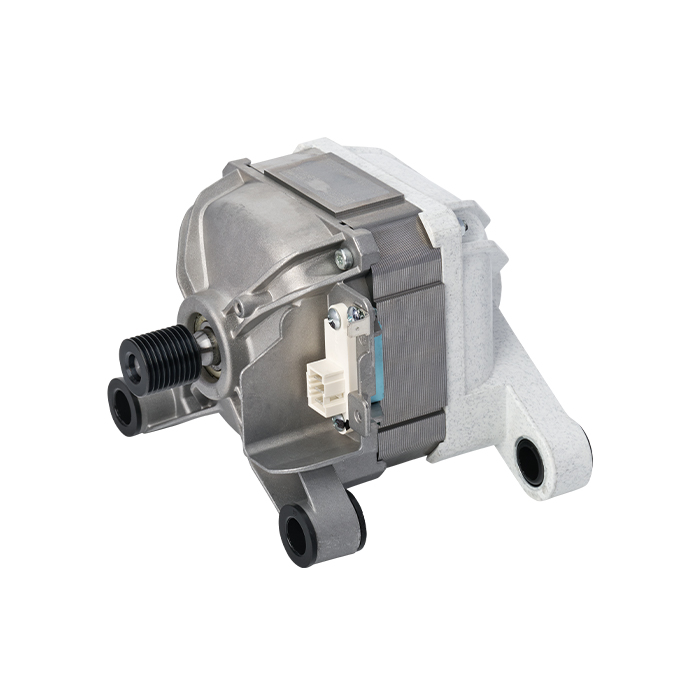
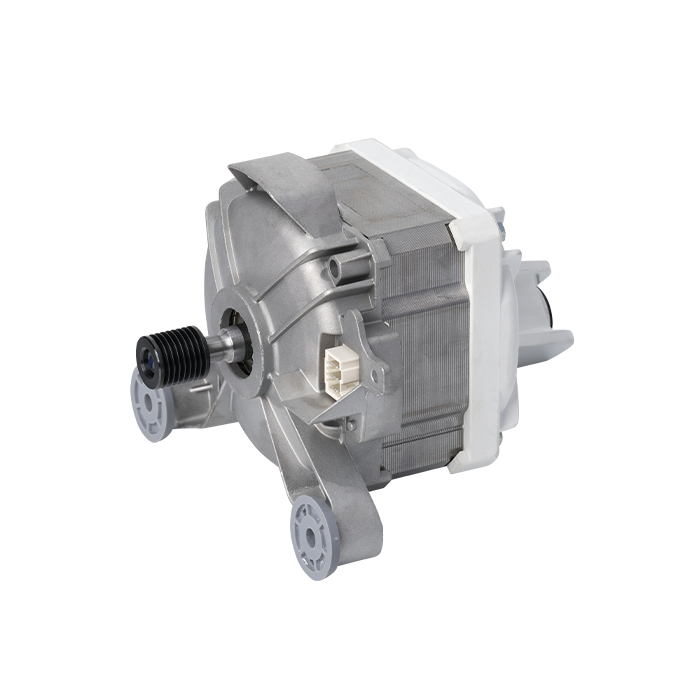
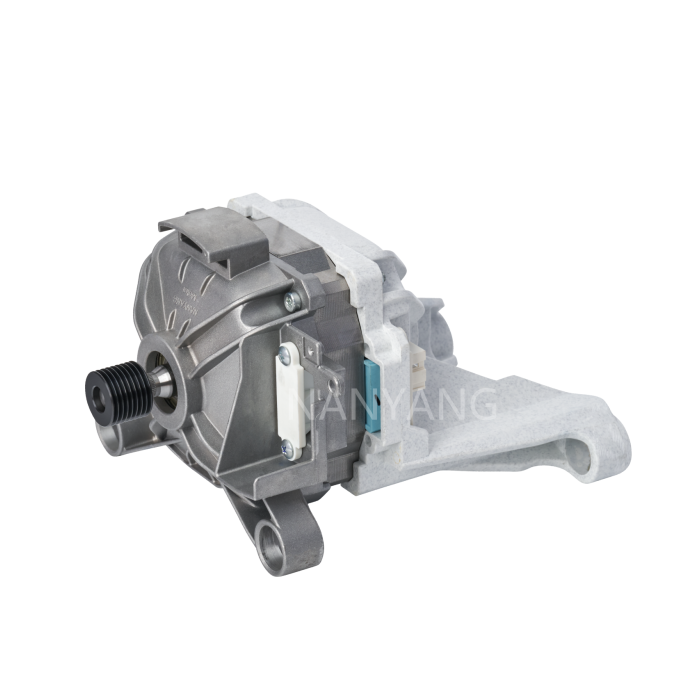
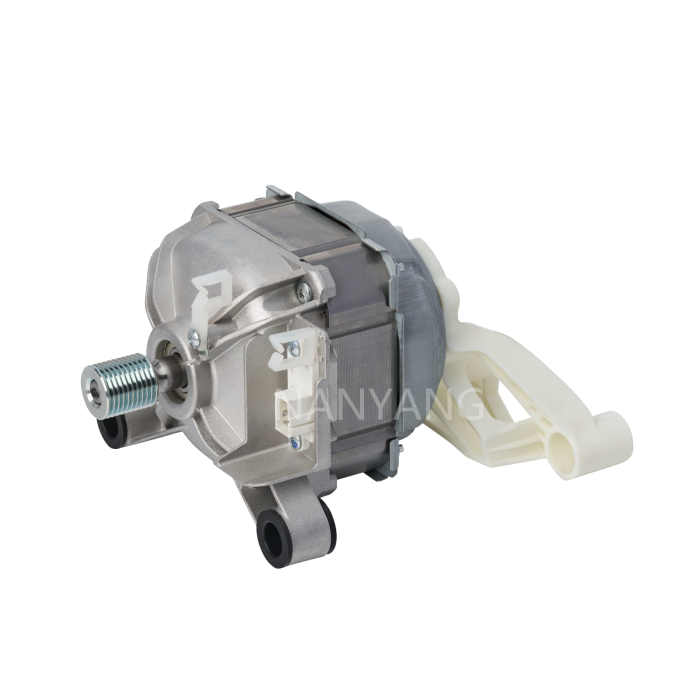
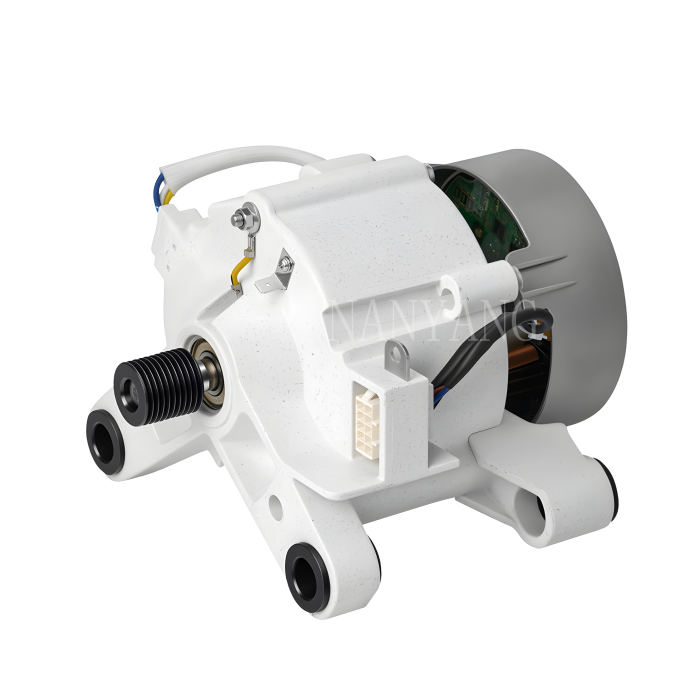
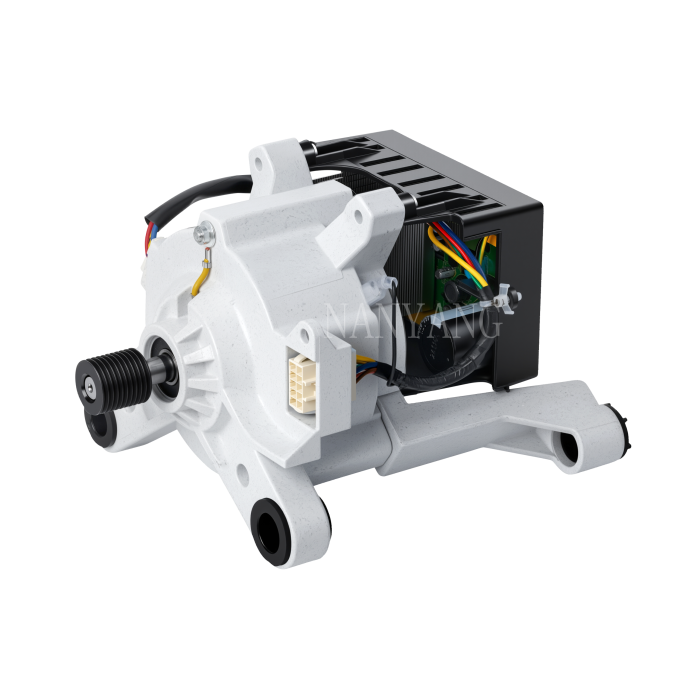
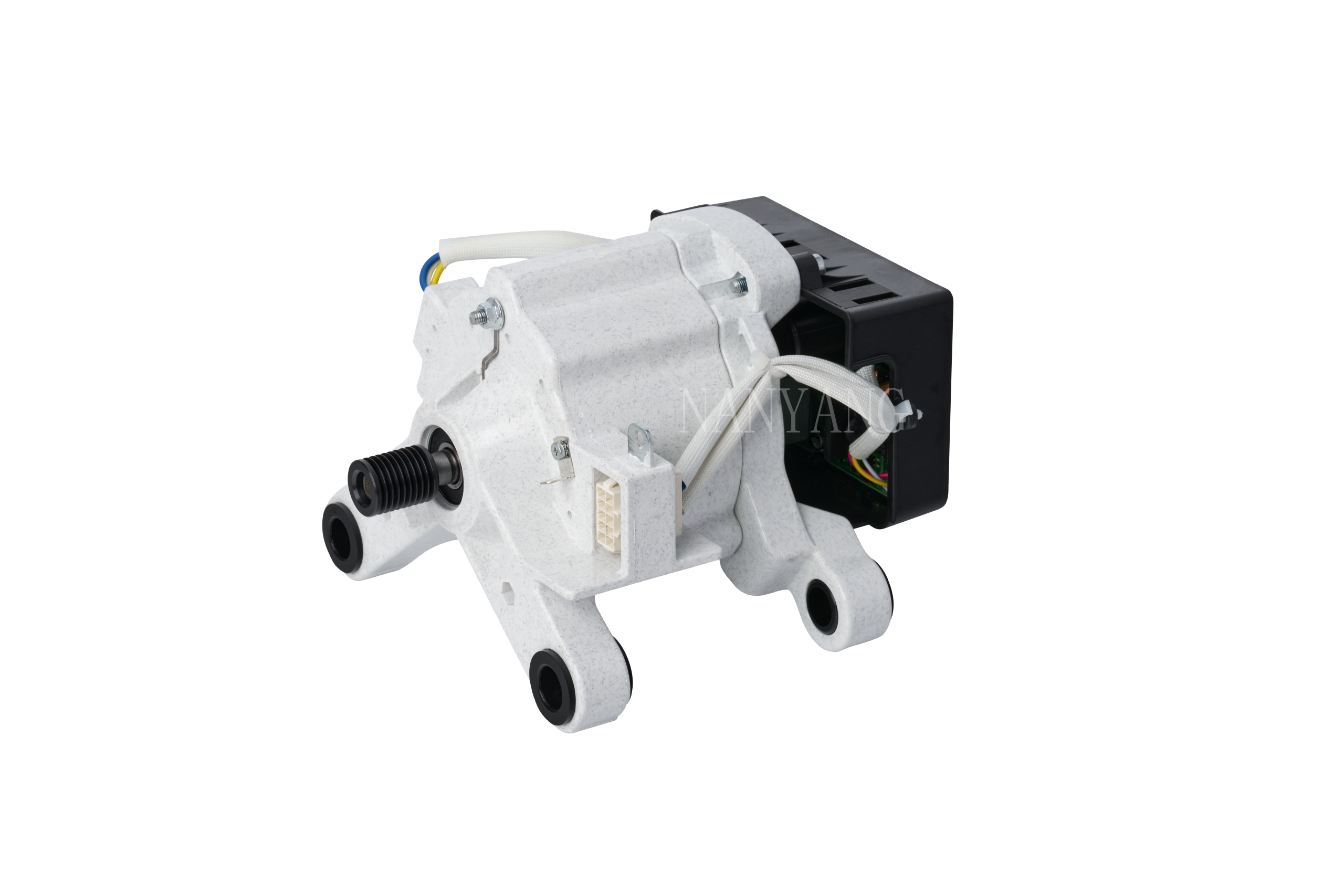
A Brushless DC (BLDC) motor works on the basis of electronic commutation technology, which does away with the mechanical brushes and commutator assemblies that are essential components in conventional DC motors. For a BLDC motor, its stator – the fixed component of the motor structure – is made up of copper windings supplied with electric power by a dedicated motor controller. This controller modulates the current supply to the stator windings in a specific sequential manner, which further forms a continuously rotating magnetic field. The rotor, as the motor’s rotating part, is usually fitted with permanent magnets; these magnets produce magnetic interactions with the stator’s magnetic field, and such magnetic force drives the rotor to rotate steadily.
Without brushes inside the motor, friction and component wear are greatly minimized, and regular maintenance requirements are also reduced accordingly. These structural advantages enable BLDC motors to achieve an extended service life while maintaining stable and high operational efficiency.
BLDC motors come with multiple prominent benefits, such as superior energy efficiency, low noise during operation and precise speed regulation capability. What’s more, they emit far less heat during working process than traditional brushed DC motors, which makes this type of motor a perfect choice for various application scenarios that demand high operational precision and consistent reliability.
 Contact
Us
Contact
Us